Listen, the trading game has changed. If you’re still clicking buttons manually, you’re falling behind. Automation is king. But not all automation is created equal. You’ve got trading bots, and you’ve got AI agents. Understanding the difference between Trading Bots vs. AI Agents isn’t just academic; it’s the key to making serious money in 2025 and beyond. This guide cuts the fluff and shows you exactly what each can do, their limitations, and how to use them to your advantage.

🤖 What Are Trading Bots? The Rule-Based Workhorses
A trading bot is essentially a piece of software programmed to execute trades automatically based on a predefined set of rules. Think of it as a tireless, emotionless order-placer. You tell it what to do, and it does it, 24/7.
Executing Predefined Strategies:
The core of a trading bot is its strategy, which is coded as a set of specific rules. These rules are usually based on technical indicators, price levels, or specific market conditions. For example:
- “If the 50-period moving average crosses above the 200-period moving average, AND the RSI is above 50, then buy X amount.”
- “If the price hits X support level, then buy. If it hits Y resistance level, then sell.”
The bot doesn’t think; it simply follows these ‘if-then’ instructions without deviation.
Common Use Cases:
Trading bots are incredibly useful for tasks that require speed, consistency, and continuous monitoring:
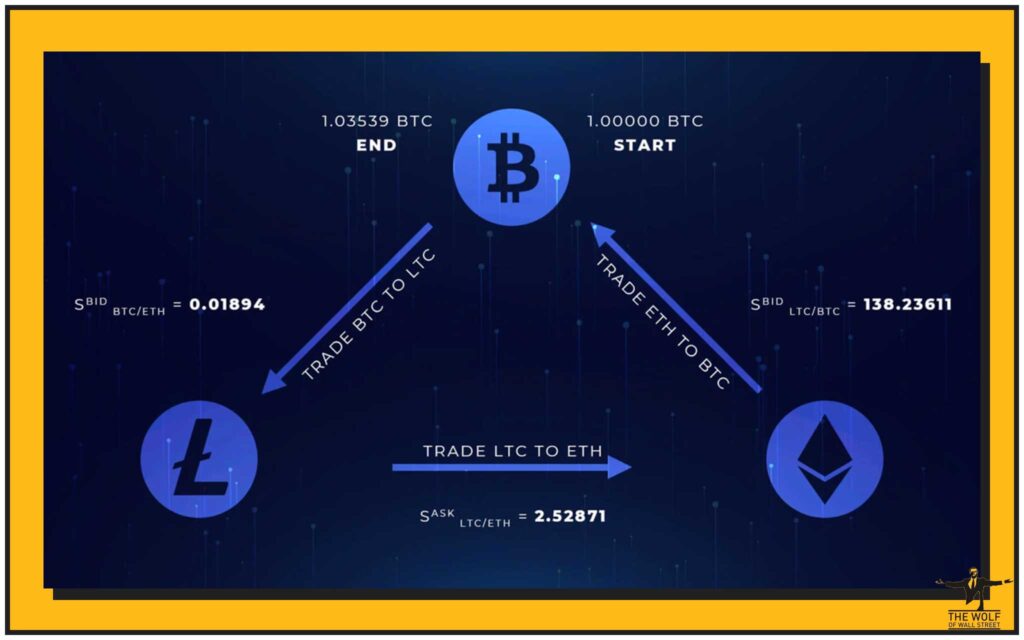
- Arbitrage: Exploiting tiny price differences for the same asset across different exchanges. Bots can spot these and execute trades in milliseconds to capture the profit.
- Trend-Following: Implementing strategies based on indicators like Moving Averages or MACD. Bots can monitor these indicators and trade crossovers or other signals as soon as they occur.
- Market-Making: Providing liquidity to an exchange by constantly placing buy and sell orders around the current market price, profiting from the bid-ask spread.
Strengths:
- Speed: Bots can execute trades much faster than any human. This is critical in fast-moving markets like Cryptocurrencies.
- Consistency: They follow their programming flawlessly, removing the emotional element of trading (fear, greed) that often leads to mistakes.
- 24/7 Operation: Bots never sleep, get tired, or take breaks. They can monitor markets and execute trades around the clock, which is essential for global crypto markets.
Limitations:
- Rigidity: This is their biggest weakness. Bots stick to their rules, even if market conditions change dramatically and those rules are no longer effective. They can’t adapt to new information or unexpected events.
- Inability to Learn: A standard trading bot doesn’t learn from its past trades or improve its strategy over time based on experience. It just keeps executing the same code.
- Vulnerability to Errors: A bug in the code or a poorly designed strategy can lead to significant losses. The bot will diligently execute bad instructions.
🧠 What Are AI Agents? The Adaptive Brains
AI agents in trading represent a significant step up in sophistication. These aren’t just rule-followers; they use artificial intelligence, particularly machine learning (ML), to analyse data, make predictions, and adapt their strategies.

Leveraging Machine Learning and Data Analysis:
AI agents are designed to learn from historical and real-time market data. They employ various machine learning algorithms (like regression, classification, or reinforcement learning) to identify complex patterns, correlations, and potential future price movements that a human or a simple bot might miss.
Key Capabilities:
- Predictive Analysis: AI agents can attempt to forecast potential price movements or trend changes with a certain probability based on the patterns they’ve learned.
- Sentiment Evaluation: Some AI agents can process vast amounts of unstructured data, such as news articles, social media posts, and forum discussions, to gauge market sentiment (bullish, bearish, fearful, greedy) and factor that into trading decisions.
- Dynamic Risk Management: Advanced AI agents can adjust position sizes, stop-loss levels, or even entire strategies based on evolving market volatility or perceived risk.
Data Sources:
Unlike simple bots that might only look at price and volume, AI agents can consume a much wider range of data:
- Market Data: Price, volume, order book depth, volatility.
- Alternative Data: News feeds (e.g., Reuters, Bloomberg), social media trends (Twitter, Reddit), economic reports, geopolitical events, and even satellite imagery or weather data for commodity-related AI.
Strengths:
- Adaptability: This is the primary advantage. AI agents can potentially adapt their strategies to changing market conditions, learning from new data as it comes in.
- Learning from Data: They can (in theory) improve their performance over time by identifying which patterns or signals lead to profitable outcomes.
- Complex Pattern Recognition: AI can identify subtle, non-linear relationships and correlations in vast datasets that are beyond human analytical capabilities or the simple rules of a bot.
Limitations:
- Data Dependency: The performance of an AI agent is heavily reliant on the quality, quantity, and relevance of the data it’s trained on. Biased or insufficient data leads to poor models.
- “Black Box” Behavior: The decision-making processes of complex AI models (especially deep learning) can be opaque. It can be difficult to understand why an AI agent made a particular trade, making it hard to debug or trust.
- High Computational Costs: Training and running sophisticated AI models requires significant computing power and specialised hardware, which can be expensive.
- Overfitting: A common problem where an AI model learns the noise and specific quirks of historical data too well, leading to excellent performance on past data but poor performance in live, unseen market conditions.
⚔️ Trading Bots vs. AI Agents: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Let’s break down the core differences to make it crystal clear.
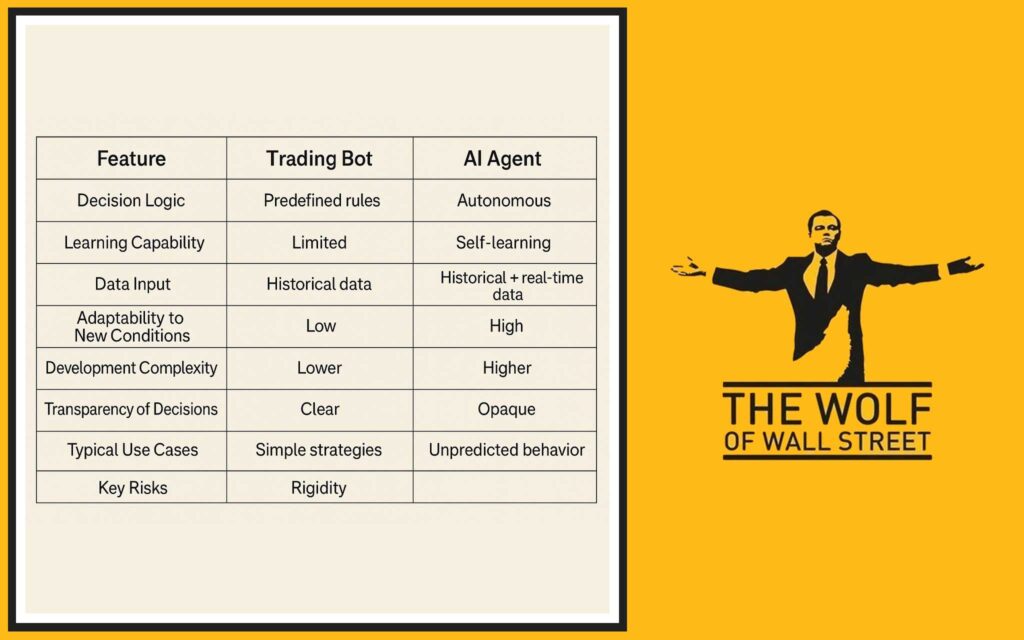
- Adaptability and Learning:
- Bots: Static. Follow predefined rules. Do not learn or adapt.
- AI Agents: Dynamic. Can learn from data and adapt strategies.
- Complexity and Development:
- Bots: Relatively simpler to develop and deploy if the strategy is clear.
- AI Agents: Highly complex, requiring expertise in data science, machine learning, and significant development time.
- Data Processing Capabilities:
- Bots: Typically use structured market data (price, volume, indicators).
- AI Agents: Can process vast amounts of structured and unstructured data (news, social media, etc.).
- Risk Profiles:
- Bots: Risk of strategy becoming outdated, programming errors, failure in unexpected market events.
- AI Agents: Risk of model overfitting, data quality issues, “black box” errors, high computational costs.
- Best Use Cases for Each:
- Bots: High-frequency arbitrage, market making, simple rule-based trend following or range trading, executing trades based on signals from other analysis (including AI).
- AI Agents: Complex pattern recognition, predictive modelling, sentiment analysis, dynamic strategy adaptation, portfolio optimisation.
⚠️ Risks in Automated Trading: Know What You’re Facing
Automated trading isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it path to riches. Both bots and AI agents come with significant risks that can wipe you out if you’re not careful.
Common Risks with Trading Bots:
- Programming errors: A simple typo or logical flaw in the bot’s code can lead to disastrous trades, repeated losses, or failure to execute critical stop losses.
- Market regime changes: A bot programmed for a trending market (e.g., using Moving Averages) will likely perform poorly or generate losses if the market suddenly shifts into a sideways, choppy range. The bot won’t know the difference.
- Connectivity and Platform Issues: Bots rely on stable connections to exchanges. API downtimes, exchange outages, or sudden changes in trading rules can cause bots to malfunction.
Specific Risks with AI Agents:
- Overfitting to historical data: This is a huge one. An AI model might look brilliant in backtests because it has learned the specific noise and patterns of the past data too well. When deployed in live trading with new, unseen data, it fails spectacularly.
- Data quality and “garbage in, garbage out”: AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. Biased, incomplete, or inaccurate data will lead to flawed models and bad trading decisions.
- “Black Box” decisions: As mentioned, the inner workings of some complex AI models can be opaque. If an AI agent starts making strange trades, it can be incredibly difficult to diagnose why or what to fix.
- Cybersecurity threats: Sophisticated AI systems can be targets for advanced cyberattacks, potentially compromising strategies or funds.
Real-World Failure Scenarios:
(Imagine describing a generic bot failure): “Consider a flash crash scenario. A simple trend-following bot, not programmed for extreme volatility, might interpret the rapid drop as a new, strong downtrend and open large short positions right at the bottom, only to be hit with massive losses when the price sharply rebounds.”
(Imagine describing a generic AI failure): “An AI agent trained on news sentiment might misinterpret a sarcastic or complex news headline about a company or Cryptocurrencies asset, taking a large position based on a flawed sentiment reading, leading to unexpected losses when the true market reaction becomes clear.”
🛠️ Leading Platforms and Tools in 2025
The market for automated trading tools is constantly evolving. Here are some examples of platforms and tools traders are using:
Examples of Bot Platforms:
Many platforms offer user-friendly interfaces to create and deploy rule-based trading bots without needing to code:
- Pionex: Known for its built-in trading bots like grid trading bots and arbitrage bots.
- Cryptohopper: Offers a marketplace for strategies, social trading features, and bot creation tools.
- 3Commas: Provides tools for smart trading, including bots for various strategies like DCA, grid, and options.
Examples of AI-Driven Tools/Platforms:
True AI agents are more complex and often proprietary, but some platforms offer AI-assisted features:
- Trade Ideas’ HOLLY AI: A well-known AI engine in stock trading that suggests trades based on its analysis of market patterns.
- TrendSpider: Uses AI and machine learning to automate technical analysis tasks like trendline detection and pattern recognition.
- Emerging AI solutions: Many firms are developing AI-powered analytics, signal generation services, and portfolio management tools. Accessing these often requires significant capital or expertise. For many, the journey starts with understanding market fundamentals from trusted Trading Insights.
🤝 The Hybrid Strategy: The Optimal Approach for 2025?

So, is it bots OR AI? The smart money says it’s bots AND AI. The most powerful approach emerging for 2025 is the hybrid strategy – combining the strengths of both.
Leveraging Bot Consistency for Execution.
Use trading bots for what they do best: executing trades based on clear, predefined rules with speed and precision. They are the tireless order-placers, managing entries, exits, and stop losses without emotion. A bot can execute a strategy derived from complex technical indicators like RSI or Bollinger Bands flawlessly.
Using AI Adaptability for Strategy and Analysis.
Employ AI agents for higher-level tasks:
- Analysing vast market data to identify emerging trends or anomalies.
- Generating or refining trading strategies based on learned patterns.
- Assessing real-time market sentiment.
- Dynamically adjusting risk parameters for bots based on perceived market conditions.
How Bots and AI Complement Each Other.
In a hybrid system, the AI acts as the ‘brain’, performing complex analysis and making strategic decisions. The bot acts as the ‘hands’, executing those decisions and managing trades with mechanical precision. This allows traders to benefit from AI’s adaptability without sacrificing the reliability and speed of rule-based execution.
Real-World Case Studies of Hybrid Success:
(Describe generic examples or reference firm types): “Top quantitative hedge funds have been using hybrid approaches for years. They might use sophisticated AI models to develop broad market theses or identify mispriced assets, then deploy an army of specialized bots to execute trades based on those insights across different markets and timeframes. Similarly, advanced retail platforms are starting to offer AI-generated signals that users can then choose to automate with configurable bots.” Firms that combine deep research, like that discussed in guides to Research Crypto Opportunities, with automated execution often gain an edge.
🚶♂️ Transitioning to Hybrid Systems: Actionable Steps
Moving from simple bots, or manual trading, to AI-assisted or fully hybrid systems is a significant step.
Assessing Your Current Setup and Needs:
- What are your trading goals? (Short-term, long-term, specific strategies?)
- What are your technical skills and resources? (Can you code, manage complex systems, afford AI tools?)
- What are the limitations of your current approach that you’re trying to solve?
Technical and Operational Considerations:
- Data Pipelines: AI needs access to high-quality, clean data. How will you source, store, and process this?
- Integration: How will your AI components communicate with your execution bots?
- Infrastructure: Do you have the necessary computing power and low-latency connections?
- Backtesting: Rigorous backtesting of hybrid strategies is even more critical due to the increased complexity.
Risk Management for Hybrid Systems:
- Model Risk: Understand the limitations and potential failure points of your AI models.
- Systemic Risk: How do the different components (AI and bots) interact? What happens if one part fails?
- Monitoring: Hybrid systems still require careful monitoring. Don’t assume it’s fully “set and forget.”

⚖️ Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The rise of automated and AI-driven trading brings new regulatory and ethical questions that are still being debated.
Evolving Regulatory Scrutiny: How authorities are looking at automated trading and AI.
Regulators globally are trying to catch up with the speed of technological development. Concerns include market stability, potential for manipulation by sophisticated algorithms, and investor protection. Expect more scrutiny and specific regulations for automated trading systems.
Transparency and Explainability of AI Decisions: The challenge of “black box” models.
If an AI agent makes a series_of bad trades, it’s crucial to understand why. But the “black box” nature of some AI models makes this difficult. The push for ‘Explainable AI’ (XAI) in finance is growing, aiming to make AI decisions more transparent and auditable.
Ethical Implications of AI in Markets: Market manipulation, fairness, and accountability.
Questions arise about fairness if AI gives certain market participants an insurmountable advantage. Who is responsible if an AI system causes a market disruption or significant losses due to unforeseen behaviour? These are complex ethical issues without easy answers yet. The broader Ecosystems of digital finance are grappling with these.
Glossary of Key Automated Trading Terms:
To navigate this space, understanding some key jargon is essential:
- Arbitrage: Profiting from price differences of the same asset on different markets.
- Sentiment Analysis: Using AI to analyse text (news, social media) to gauge market mood.
- Overfitting: When an AI model learns historical data too well, including its noise, leading to poor performance on new data.
- Black Box Model: An AI system whose internal workings and decision-making processes are opaque to its users or even its developers.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI where systems learn from data without being explicitly programmed for each task.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Algorithmic trading characterized by extremely high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios.
- Backtesting: Testing a trading strategy on historical data to see how it would have performed.
- Latency: The delay in data transmission. Low latency is critical for HFT and arbitrage bots.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the main difference between a trading bot and an AI agent?
A trading bot executes trades based on predefined, static rules, while an AI agent uses machine learning to analyse data, learn, and adapt its strategies. - Can AI agents predict market movements with certainty?
No, AI agents provide probabilistic forecasts based on patterns learned from data. They cannot predict markets with certainty; they aim to improve the odds. - What are the biggest risks of using simple trading bots?
The biggest risks are their rigidity (inability to adapt to changing market conditions) and their vulnerability to programming errors or outdated strategies. - What is “overfitting” in the context of AI trading agents?
Overfitting occurs when an AI model learns the specific noise and details of its training data too well, causing it to perform poorly when faced with new, live market data. - What is a “hybrid strategy” in automated trading?
A hybrid strategy combines the strengths of both trading bots (for reliable, fast execution) and AI agents (for adaptive analysis, strategy generation, and risk management).
The bottom line on Trading Bots vs. AI Agents? Bots are your tireless soldiers; AI is your adaptive general. For 2025, using both is how you conquer the markets.
“The Wolf Of Wall Street crypto trading community offers a comprehensive platform for navigating the volatile cryptocurrency market. Here’s what you gain:
- Exclusive VIP Signals: Access proprietary signals designed to maximize trading profits.
- Expert Market Analysis: Benefit from in-depth analysis from seasoned crypto traders.
- Private Community: Join a network of over 100,000 like-minded individuals for shared insights and support.
- Essential Trading Tools: Utilize volume calculators and other resources to make informed decisions.
- 24/7 Support: Receive continuous assistance from our dedicated support team./n/nEmpower your crypto trading journey:
- Visit our website: https://tthewolfofwallstreet.com/ for detailed information.
- Join our active Telegram community: https://t.me/tthewolfofwallstreet for real-time updates and discussions.
- Unlock your potential to profit in the crypto market with “The Wolf Of Wall Street””





