Listen up. The crypto market just got a major upgrade. Forget the old barriers. Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs are here, opening up crypto to mainstream investors without direct ownership. This isn’t just a convenience; it’s a powerful, regulated investment option reshaping how the world accesses digital assets. Get this breakdown, and you’ll be on the right side of history.

🚀 Executive Summary (TL;DR)
- Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs offer regulated, accessible exposure to major cryptocurrencies via traditional exchanges.
- They allow investors to participate in crypto price movements without direct custody of digital assets.
- Key differences include market maturity, underlying blockchain use cases, and AUM.
- Both come with market volatility and regulatory risks, but provide diversification benefits.
- Understanding their structure, fees, and tax implications is vital for informed decisions.
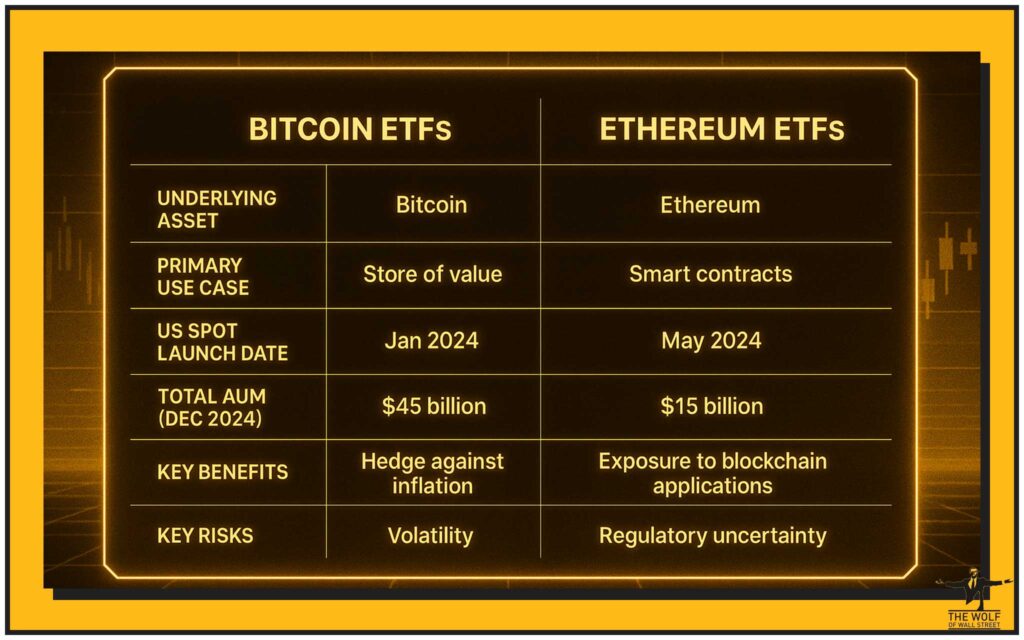
👑 Bitcoin ETFs: The Pioneer’s Regulated Access
Bitcoin, the world’s first and largest cryptocurrency, has been a financial phenomenon. For years, investors wanting exposure had to directly buy and secure the digital asset. Not anymore. Bitcoin ETFs changed that, providing a regulated, accessible avenue for broad participation.
Purpose: Tracking Bitcoin’s Performance.
The primary purpose of a Bitcoin ETF is straightforward: to track the price performance of Bitcoin as closely as possible. This allows investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin’s price movements through a traditional brokerage account, just like buying shares of a company. It removes the complexities of self-custody, managing crypto wallets, or dealing with less regulated crypto exchanges.
Milestones: Futures ETF (BITO 2021), Spot ETF Approval (Jan 2024).
The journey to mainstream acceptance for Bitcoin ETFs has been marked by significant milestones:
- The first Bitcoin futures ETF, the ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (ticker BITO), launched in October 2021 in the United States. This ETF held Bitcoin futures contracts, not actual Bitcoin, and was the first regulated way for US investors to get Bitcoin exposure via ETFs.
- The watershed moment arrived in January 2024 when the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved 11 spot Bitcoin ETFs from major financial institutions. This marked a profound step toward mainstream adoption, as these ETFs hold actual Bitcoin, making them more direct and attractive to institutional capital.
Growth: AUM surpassing Gold ETFs ($129+ billion Dec 2024).
The growth of Bitcoin ETFs has been explosive, especially after the spot approvals. As of December 2024, Bitcoin ETFs collectively commanded over $129 billion in assets under management (AUM). This rapid accumulation of capital saw them surpass the AUM of US gold ETFs, a traditional inflation hedge, highlighting the massive demand for regulated digital asset exposure. This growth is a clear signal of institutional and retail confidence.
Examples of Leading Bitcoin ETFs:
Several prominent financial players launched spot Bitcoin ETFs, leading to a competitive market:
- ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF (ARKB)
- VanEck Bitcoin Trust (HODL)
- iShares Bitcoin Trust ETF (IBIT) from BlackRock, which quickly became a dominant offering due to BlackRock’s immense size and influence.
- Franklin Bitcoin ETF (EZBC)
- Bitwise Bitcoin ETF Trust (BITB)
How They Work: Direct Holding vs. Derivatives (Futures).
Bitcoin ETFs operate in one of two ways:
- Spot ETFs: These ETFs hold Bitcoin directly. When you buy a share of a spot Bitcoin ETF, you are buying a share of a fund that actually holds Bitcoin in cold storage, often with regulated custodians. This offers direct price exposure with lower tracking error.
- Futures ETFs: These ETFs invest in Bitcoin futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell Bitcoin at a future date at a predetermined price. While they provide exposure, they can be subject to ‘contango’ (where futures prices are higher than spot prices), leading to potential tracking error.
Benefits: Regulation, Accessibility, Diversification, Relative Stability.
- Regulation: ETFs operate under established financial regulations, providing an added layer of investor protection and oversight.
- Accessibility: They trade on traditional stock exchanges, making them easily accessible through standard brokerage accounts without the need to use crypto-specific platforms.
- Diversification: While gaining exposure to Bitcoin, holding an ETF in a broader portfolio of traditional assets can offer diversification benefits due to Bitcoin’s unique correlation patterns.
- Relative Stability: Compared to direct crypto markets, the regulated nature and larger liquidity pools of ETFs can provide a somewhat more stable trading environment for price exposure.
Risks: Volatility, Regulatory Uncertainty, Tracking Error, Competition, Limited Supply.
- Volatility: Despite the regulated wrapper, Bitcoin ETFs are still subject to the inherent, rapid price changes of Bitcoin itself.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: While US spot ETFs are approved, the broader regulatory landscape for Cryptocurrencies remains dynamic and could still impact the underlying asset or future product offerings.
- Tracking Error: Especially for futures-based ETFs, there’s a risk that the ETF’s performance might not perfectly match the underlying Bitcoin price due to fees, operational costs, or contract rollovers.
- Bitcoin-specific: Bitcoin faces competition from other cryptocurrencies and its limited supply can lead to sharp price movements, impacting ETF value.
🏰 Ethereum ETFs: The Smart Contract King’s Mainstream Debut
Following Bitcoin’s success, Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency and the foundation for decentralised applications (DApps), also gained its mainstream entry via ETFs.
Purpose: Provide Exposure to Ethereum’s Ecosystem.
Ethereum ETFs allow investors to gain exposure to Ethereum’s price movements without directly owning Ether. This is particularly appealing given Ethereum’s role as the backbone for a vast ecosystem of decentralised finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and other blockchain applications.
Milestones: Spot Ether ETF Approval (July 2024).
The SEC’s approval of nine spot Ether ETFs in July 2024 was a significant follow-up to the Bitcoin ETF approvals. This move solidified Ethereum’s position as the second cryptocurrency with ETF representation in US markets, signaling growing acceptance of the broader digital asset space.
Growth: AUM ($14+ billion Dec 2024).
Since their approval, Ethereum ETFs have also seen substantial growth. By December 2024, these ETFs had accumulated about $14 billion in assets under management (AUM), reflecting growing institutional and retail interest in Ethereum’s ecosystem and its price potential.

Examples of Leading Ethereum ETFs:
Major financial institutions were quick to offer Ethereum ETFs:
- Fidelity Ethereum Fund (FETH)
- Bitwise Ethereum ETF (ETHW)
- VanEck Ethereum ETF (ETHV)
- ProShares Ether Strategy ETF (EETH)
- 21Shares Core Ethereum ETF (CETH)
- Franklin Templeton Ethereum ETF (EZET)
How They Work: Direct Holding vs. Derivatives.
Similar to Bitcoin ETFs, Ethereum ETFs can operate by holding actual Ether (spot ETFs) or by using Ethereum futures contracts (futures ETFs) to mirror its price performance. The preference is generally for spot ETFs due to lower tracking error and more direct exposure.
Benefits: Exposure to DeFi and NFTs, Innovation, Regulated Access, Diversification (blockchain tech).
- Exposure to DeFi and NFTs: Ethereum ETFs offer a way for traditional investors to participate in the growth of these innovative sectors without directly interacting with complex DeFi protocols or NFT marketplaces.
- Innovation: Ethereum is a platform for constant innovation in blockchain technology. Investing in an Ethereum ETF gives exposure to this broader technological advancement.
- Regulated Access: Like Bitcoin ETFs, they provide a regulated pathway to invest through traditional brokerage accounts.
- Diversification: For investors already holding Bitcoin, an Ethereum ETF can offer diversification into a different segment of the crypto market (smart contract platforms).
Risks: Volatility, Regulatory Uncertainty, Tracking Error, Reliance on DeFi/NFT Growth, Technical Upgrades.
- Volatility: Ethereum’s price is highly volatile, similar to Bitcoin.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory status of Ethereum (e.g., whether it might be considered a security) continues to be debated, which could impact its ETFs.
- Tracking Error: Futures-based Ether ETFs can experience tracking error.
- Reliance on DeFi/NFT Growth: Ethereum’s value is closely tied to the success and growth of its ecosystem. A downturn in DeFi or NFTs could impact Ether’s price.
- Technical Risks from Upgrades: Ethereum undergoes significant technical upgrades (like the Merge). While designed to improve the network, complex upgrades carry inherent technical risks that could affect the asset.
⚔️ Key Differences: Bitcoin vs. Ethereum ETFs
While both offer crypto exposure, there are fundamental differences investors must consider.
- Underlying Asset and Use Cases:
- Bitcoin ETFs: Are primarily tied to Bitcoin, which is often viewed as ‘digital gold’ or a store of value. Its primary use case is as a decentralised, censorship-resistant digital currency.
- Ethereum ETFs: Are tied to Ethereum, which serves as a foundational platform for smart contracts, decentralised applications (DApps), and is the backbone of the DeFi and NFT sectors. Its utility is broader than Bitcoin’s.
- Market Maturity and AUM:
- Bitcoin ETFs: Are more established with a longer history in futures form and a much higher AUM ($129+ billion), reflecting its first-mover advantage and wider institutional adoption.
- Ethereum ETFs: Are newer, with a smaller AUM (\~$14 billion), but are rapidly growing, indicating increasing institutional interest in Ethereum’s ecosystem.
- Launch Timeline (US):
- Bitcoin ETFs: First futures ETF in 2021, spot ETF approval in January 2024.
- Ethereum ETFs: Spot ETFs approved in July 2024, roughly six months after Bitcoin’s spot approval.
- Specific Risks:
- Bitcoin-specific: Competition from other cryptocurrencies aiming to be stores of value, and the impact of its limited supply dynamics.
- Ethereum-specific: Reliance on the continued growth and success of its ecosystem (DeFi, NFTs), and technical risks associated with its ongoing network upgrades.
💲 Performance and Fees: What You Pay, What You Get
When you invest, what you pay in fees directly impacts your net returns. Performance, while important, must be viewed net of these costs.
Comparing Expense Ratios of Leading ETFs.
All ETFs charge an expense ratio, an annual fee expressed as a percentage of your total investment. This covers the fund’s operating and management costs. Lower expense ratios mean more of your money remains invested and contributes to your returns. For instance, comparing the expense ratios of leading Bitcoin ETFs like BlackRock’s IBIT versus Fidelity’s FBTC, or competing Ether ETFs, is crucial for choosing the most cost-efficient option. Even a small difference of 0.10% can compound significantly over many years, eroding your profits.
Tracking Performance Against Underlying Assets.
ETFs aim to perfectly track the performance of their underlying asset. However, ‘tracking error’ exists. This is the difference between the ETF’s performance and the actual performance of the Bitcoin or Ethereum it holds. Factors contributing to tracking error include management fees, trading costs within the fund, and the operational inefficiencies. Spot ETFs typically have lower tracking errors than futures-based ETFs, which incur costs from rolling over expiring contracts. Evaluating how closely an ETF has historically mirrored its underlying asset is a key part of your due diligence.
Impact of Fees on Long-Term Returns.
The compounding effect of fees is a silent killer of returns. Over long periods, even small fees can significantly diminish your accumulated wealth. For example, if you hold a Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs for 10 years, a 0.25% annual fee will leave you with a substantially higher return than a 1.00% fee, assuming similar underlying asset performance. Choose low-fee ETFs when possible.
💸 Tax Implications: What You Need to Know
Don’t get caught flat-footed by taxes. Selling crypto ETFs usually means a taxable event, and understanding this is vital for your actual profit.
Capital Gains Taxes on ETF Sales.
Profits from selling Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs are typically subject to capital gains taxes, just like profits from selling traditional stocks or mutual funds. The tax rate you pay often depends on your holding period:
- Short-term capital gains: These usually apply if you hold the ETF for less than a year. They are typically taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be higher.
- Long-term capital gains: These usually apply if you hold the ETF for more than a year. They are often taxed at a lower, preferential rate.
Tax Advantages in Retirement Accounts (e.g., US 401k/IRA).
Investing in crypto ETFs within tax-advantaged retirement accounts (like 401(k)s or Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) in the US) can offer significant tax benefits. These accounts can allow for tax-deferred growth (you don’t pay taxes on gains until retirement) or even tax-free withdrawals in retirement (in the case of a Roth IRA), making them a major appeal for long-term crypto exposure for those who qualify.
Country-Specific Examples: General advice to consult local expert.
Tax implications for crypto ETFs can vary significantly by jurisdiction. It is absolutely essential to understand the specific tax regulations in your country of residence or where you are a tax resident.
- (Briefly describe: For US investors, Bitcoin ETFs in a Roth IRA can grow tax-free. For UK investors, gains might be subject to Capital Gains Tax (CGT) with an annual exempt allowance, but any profits beyond that are taxed. For EU investors, tax treatment varies by member state, with some applying income tax and others capital gains tax. Always consult a local tax advisor who specialises in crypto, as Policies around digital assets are complex and evolving.)
🏛️ Institutional Adoption & Market Impact
The arrival of spot Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs marks a watershed moment, driving unprecedented institutional capital into the crypto market and validating the asset class.
Pension Fund Investment (State of Wisconsin example).
A clear signal of mainstream acceptance came when large, typically very conservative investors, such as pension funds, started allocating to Bitcoin ETFs. For instance, the State of Wisconsin Investment Board, managing billions for public employees and retirees, publicly disclosed investments in Bitcoin ETFs like BlackRock’s IBIT and Grayscale’s GBTC. This demonstrates serious, long-term confidence from a major institutional player.
BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust Dominance ($60+ billion AUM).
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager with trillions under management, quickly established its iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) as a dominant player in the Bitcoin ETF space. Within months of its launch, IBIT accumulated over $60 billion in AUM (as of late 2024), demonstrating immense investor demand and BlackRock’s considerable influence in directing capital flows. This rapid growth reshaped the ETF landscape and signaled a strong shift in institutional interest.
Overall Impact on Market Legitimacy and Liquidity.
The influx of institutional capital through these ETFs is having a profound impact. It is significantly increasing market liquidity, which can help reduce price volatility and make it easier to execute large trades. More importantly, this institutional embrace is lending undeniable legitimacy to the crypto market, helping it transition from a niche, speculative asset class to a more mature and integrated component of the global financial system. This institutionalisation provides stronger market foundations, beneficial for general Trading Insights.
❓ Common Misconceptions & FAQs
With new products come new questions and misunderstandings. Let’s clear up some common points about Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs.
ETF Price vs. Underlying Price (Tracking Error).
A common misconception is that an ETF’s price will perfectly match the price of its underlying asset (Bitcoin or Ethereum). While ETFs aim for this, factors like management fees, trading costs, and the operational aspects of the fund can lead to a ‘tracking error’. This means the ETF’s performance might slightly deviate from the underlying asset’s performance. Also, the ETF’s market price might trade at a slight premium or discount to its Net Asset Value (NAV) due to supply and demand for the ETF shares themselves.
ETFs are Not the Same as Direct Crypto Ownership.
This is a critical distinction. While ETFs provide price exposure, you don’t own the actual Bitcoin or Ethereum. This means you cannot:
- Self-custody the crypto in your own wallet.
- Use it in Decentralised Finance (DeFi) protocols or for lending.
- Participate in staking or governance of the underlying blockchain.
- Spend it directly.
For the nuances of direct crypto ownership and related activities, understanding Bitcoin Spot vs. Derivatives Trading is important. If you want to Earn Crypto Without Selling via staking or yield farming, you need direct ownership.
The Myth of Absolute Safety.
ETFs certainly bring a layer of regulation, accessibility, and professional management. However, this does not eliminate market risk. If Bitcoin or Ethereum prices fall, the value of your ETF shares will also fall. They are regulated investment products, not risk-free ones.
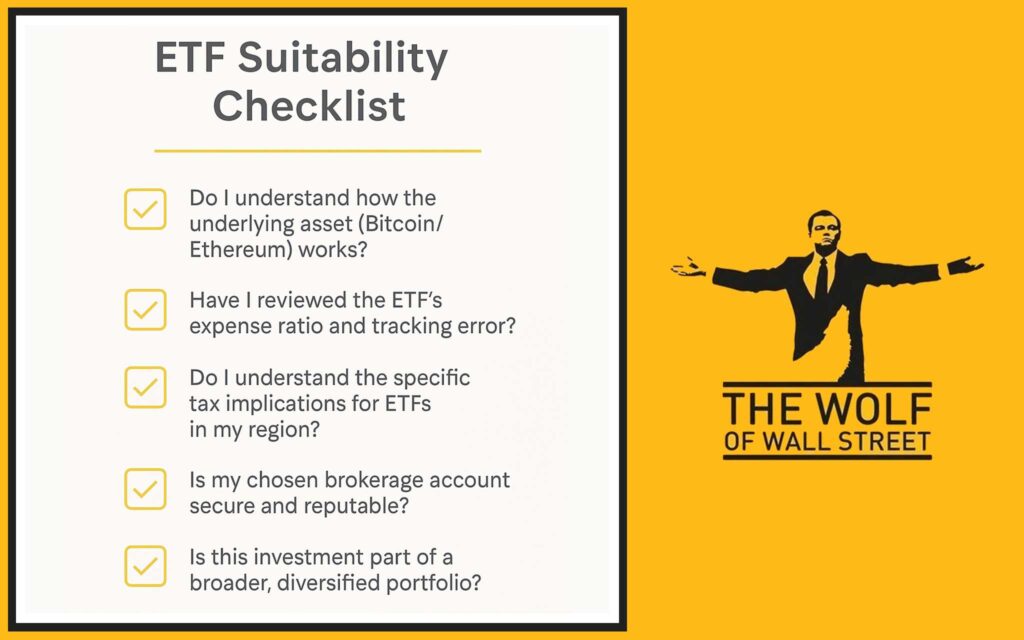
🛡️ Risk Assessment & Suitability: Is It for You?
Before investing in Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs, conduct a thorough self-assessment of your risk profile and investment goals.
Evaluating Your Risk Tolerance.
These ETFs are tied to highly volatile asset classes. Can you stomach sharp, significant price swings? Are you comfortable with potential substantial drawdowns in value? Your personal risk tolerance must align with the inherent volatility of crypto markets. If you panic during a 20% drop, these might not be for you.
Matching ETF Type to Investment Goals.
- If your goal is broad market exposure and diversification into the digital asset space, a general crypto ETF might fit.
- If you believe specifically in the future of smart contract platforms and decentralised applications, an Ethereum ETF might be your choice.
- If you view Bitcoin primarily as a store of value or ‘digital gold’, a Bitcoin ETF aligns with that narrative.
Checklist for First-Time ETF Investors.
✅ Actionable Tips for First-Time ETF Investors

Ready to jump in? Here’s how to approach investing in Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs smartly.
How to Select a Crypto ETF.
- Research the underlying asset: Understand the fundamental differences between Bitcoin’s role and Ethereum’s ecosystem. Your conviction in the underlying asset is paramount.
- Review fees: Compare the expense ratios across different providers. Look for the lowest fees, as these can significantly impact long-term returns.
- Check the structure: Prefer spot ETFs over futures-based ETFs for more direct exposure and generally lower tracking error, if available in your region.
- Look at provider reputation: Stick with ETFs offered by reputable, large financial institutions with a proven track record.
How to Buy.
You buy crypto ETFs through standard brokerage accounts, just like buying shares of any company or traditional ETF. You don’t need a crypto exchange account for direct ownership or a crypto wallet. Your broker handles the purchase and custody of the ETF shares. (For general crypto purchasing advice, you might review guides like How to Buy Crypto).
How to Monitor.
Once invested, you should regularly monitor the ETF’s price performance, its AUM, and any news related to its underlying asset (Bitcoin or Ethereum) or the ETF provider. Also, periodically check the expense ratio and tracking error to ensure the fund still meets your criteria.
Glossary of Key ETF Terms:
To help clarify the jargon in this market, here are some essential terms:
- Spot ETF: An ETF that holds the actual underlying asset (e.g., physical Bitcoin) directly.
- Futures ETF: An ETF that holds futures contracts of the underlying asset to gain exposure.
- AUM (Assets Under Management): The total market value of assets managed by a fund.
- Tracking Error: The difference between an ETF’s performance and the performance of the underlying index or asset it aims to track.
- Premium/Discount: When an ETF’s market price trades above (premium) or below (discount) its Net Asset Value (NAV).
- Expense Ratio: The annual fee charged by the fund as a percentage of the fund’s assets to cover its operating and management costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the main benefit of investing in Bitcoin or Ethereum ETFs over buying the actual crypto?
The main benefit is regulated accessibility through traditional brokerage accounts, removing the need for direct custody and crypto exchange accounts. - Are Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs completely safe from price volatility?
No, these ETFs are still subject to the inherent volatility of Bitcoin and Ethereum prices. They are regulated investment products, not risk-free ones. - Do Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs pay dividends?
Typically, no. As Bitcoin and Ethereum do not generate revenue in a way that pays dividends, their ETFs do not pay dividends either. Their value comes from price appreciation. - Can I stake Bitcoin or Ethereum if I own their ETFs?
No. When you own an ETF, you own shares of the fund, not the underlying crypto. Therefore, you cannot stake the underlying Bitcoin or Ethereum. - What is ‘tracking error’ in an ETF?
Tracking error is the difference between an ETF’s performance and the performance of the underlying asset or index it aims to track. Factors like fees and operational costs contribute to it.
There you have it – Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs. They’re not just new products; they’re your regulated gateway to the massive potential of crypto markets. Make your move.

“The Wolf Of Wall Street crypto trading community offers a comprehensive platform for navigating the volatile cryptocurrency market. Here’s what you gain:
- Exclusive VIP Signals: Access proprietary signals designed to maximize trading profits.
- Expert Market Analysis: Benefit from in-depth analysis from seasoned crypto traders.
- Private Community: Join a network of over 100,000 like-minded individuals for shared insights and support.
- Essential Trading Tools: Utilize volume calculators and other resources to make informed decisions.
- 24/7 Support: Receive continuous assistance from our dedicated support team./n/nEmpower your crypto trading journey:
- Visit our website: https://tthewolfofwallstreet.com/ for detailed information.
- Join our active Telegram community: https://t.me/tthewolfofwallstreet for real-time updates and discussions.
- Unlock your potential to profit in the crypto market with “The Wolf Of Wall Street””





